> WHAT IS THERE TO KNOW ABOUT TRACK LIGHTING?

Lighting is not just about brightness; it’s an art and science that transforms spaces, influences moods, and accentuates aesthetics. Track lighting, a versatile and dynamic lighting system, is at the forefront of this artistic endeavor. Track lighting theory is not merely about mounting fixtures on a rail; it’s a captivating fusion of design, engineering, and creativity that empowers us to sculpt light with precision. Whether you’re looking to enhance your living space or seeking to master the intricacies of this versatile system, this webpage is your gateway to know more about it.
Table of Contents
> 1. LOW VOLTAGE TRACK AND 3-PHASE TRACK LIGHTING
Track lighting is a versatile and popular choice for lighting spaces, and is available in options including low voltage and 3 groups, also often called 3 phases. Here we take a closer look at everything you need to know about low-voltage and 3-phase track lighting systems.
> 1.1. low voltage Track Lighting:
Single circuit, with or without data: low-voltage rails are equipped with a single circuit, which means that all luminaires on the rail are controlled simultaneously. When you turn the track on or off, all fixtures connected to it respond at the same time. There are also low-voltage single-circuit rails with a data line. It is possible to place DMX or Casambi controlled fixtures on this, for example, making it possible to program the fixtures in such a way that they no longer respond at the same time.
> 1.2. 3-Phase Track Lighting:
- Three circuits, with or without data: 3-phase track lighting systems consist of three separate circuits within the same section of track. Each circuit can be controlled independently, allowing areas of lighting and control of different parts of the track to be precisely defined. You can often choose phase 1, 2 or 3 on the fixtures. Here too, you can choose an extra data line for certain operating systems.
> 1.3. Both systems
- Easy to Install: Rail systems are relatively easy to install and require minimal wiring complexity.
- Fixture compatibility: rail systems are compatible with a wide range of luminaires, including advanced options such as adjustable spotlights, zoom spotlights, and RGB luminaires.
- High load capacity: rail systems can carry higher loads, making them suitable for large spaces with many fixtures.
The choice between low-voltage and 3-phase rail systems depends on the choice of fixtures. Each fixture usually indicates what the options are in terms of rails.
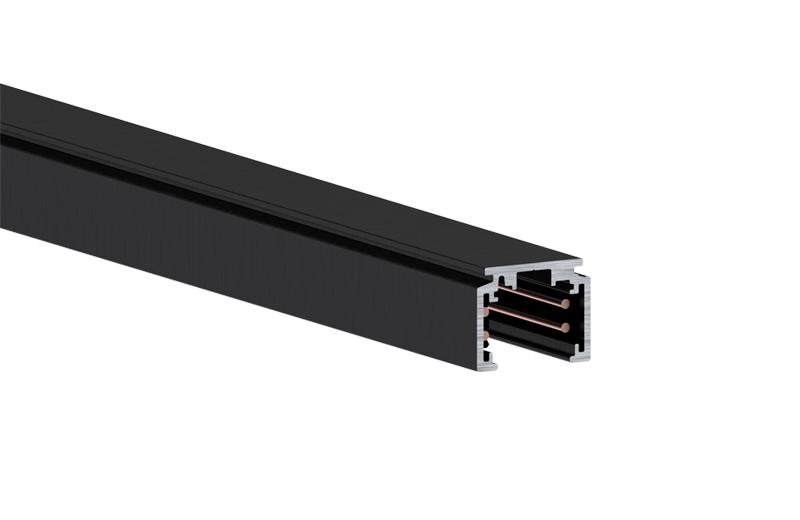
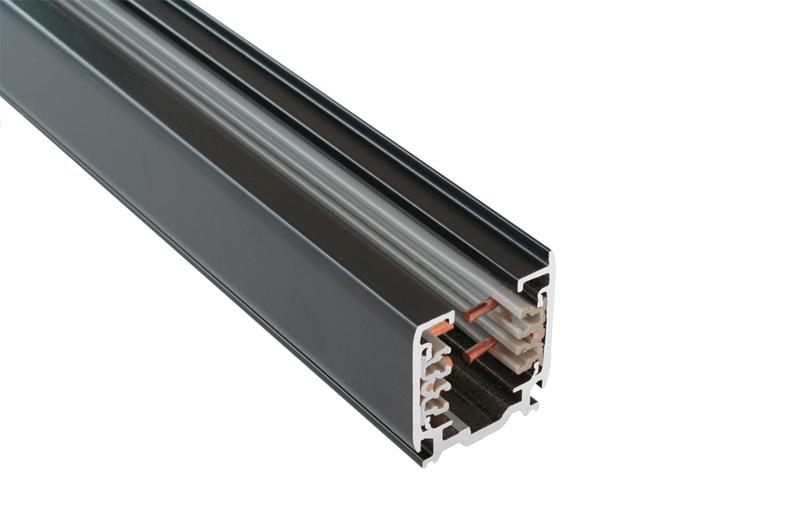


> 2. RAIL COUPLERS: T, X, L pieces
Rail couplings are connectors that join sections of rail together. In the context of electrical rail systems, these couplings ensure the continuity of electrical conductors and support the secure and reliable transmission of electricity. Rail couplings come in various designs, including bolted connections, and clamps, depending on the specific requirements of the rail system.
The choice of rail coupling is critical for maintaining electrical integrity, preventing power losses, and ensuring safety. Proper installation and maintenance of rail couplings are essential to minimize electrical resistance and maintain system reliability.
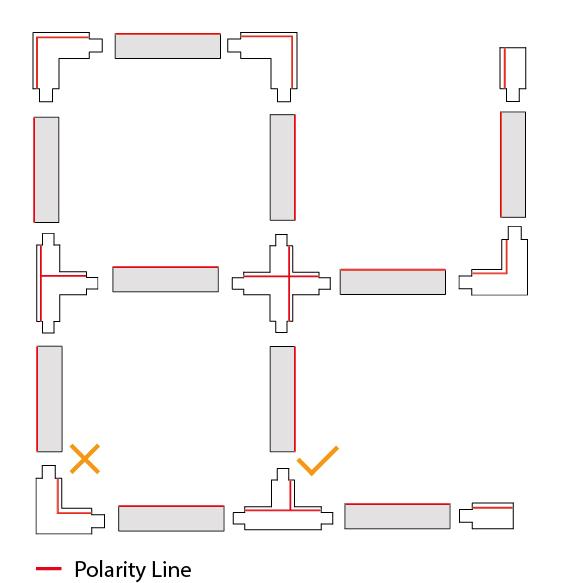
You can get pieces of rail in different lengths. The most generic lengths vary between 1–3 metres. To connect these, you can use X, T or L pieces, to make the grid as you want it to be. When you’re going to work with rail couplings, you need to make sure the line on the rails keeps going. This is to ensure that the + and – sides are not mixed. The track lighting won’t work if that is the case. See the image for the right for an example of installing the rail the correct and incorrect way.
> 3. GROUNDING OF RAIL SYSTEMS
Grounding is a crucial safety measure in electrical rail systems. It involves connecting the rail system to the earth or ground to protect against electrical faults and provide a safe path for fault currents. Proper grounding ensures the following:
Safety: Grounding helps prevent electric shock hazards by providing a path for fault currents to safely dissipate into the ground.
Equipment Protection: Grounding helps protect electrical equipment and appliances by diverting excessive electrical energy away from them during a fault.
Stability: Grounding contributes to the stability of the rail system by reducing the risk of voltage fluctuations and disturbances.
Grounding is typically achieved through a combination of grounding electrodes, grounding conductors, and grounding bonds that are strategically placed throughout the rail system. National and international electrical codes and standards dictate the specific grounding requirements for different types of rail systems.
> 4. POWER SUPPLY AND RAIL LIGHTING
When it comes to track lighting systems, whether low voltage or 3-phase, understanding the power supply differences is crucial for proper installation and efficient operation. These differences in power supply not only affect the electrical characteristics but also impact the flexibility and capacity of the lighting system. Let’s delve into the distinctions between low voltage and 3-phase track rails regarding their power supply:
> 4.1. low voltage Track Rails:
- Single-phase power supply: low-voltage rails are supplied with power via a single-phase electrical supply. In most residential and commercial environments, single-phase power is the standard.
- Limited power capacity: Due to their dependence on a single-phase power supply, low-voltage railway tracks have limited power capacity. This means that they are best suited for smaller to medium-sized applications where the lighting load is not excessively high.
- Advanced dimming options: Low voltage track systems, both as 3-phase, offer more advanced dimming options including leading-edge dimming and DALI (Digital Addressable Lighting Interface) control. These options provide precise control over the lighting system, allowing for customized lighting scenes and energy-saving strategies.
> 4.2. 3-Phase Track Rails:
- Three-phase supply: Three-phase rails are designed to be powered by a three-phase electrical supply, which is common in larger commercial and industrial environments. Three-phase power typically operates at higher voltages, such as 230V.
- Higher power capacity: The main advantage of three-phase rails is their ability to support higher lighting loads. They are suitable for large areas with a significant number of fixtures or where high intensity lighting is required, such as in shops, galleries or industrial facilities.
- Complexity and professional installation: Due to the higher voltage and complexity of three-phase power, the installation of three-phase busbars is more complicated and usually requires the expertise of a qualified electrician. These systems are better suited to larger commercial and industrial environments, where professional installation is the norm.
- Advanced dimming options: 3-phase track systems also offer advanced dimming options, allowing precise control of lighting scenes and enabling energy-saving strategies.
In summary, the main difference in power supply between low-voltage and three-phase rails lies in the number of electrical phases they use. Low-voltage rails operate on a single-phase supply, making them suitable for simpler installations with lower power requirements, such as in homes and some smaller commercial spaces. Three-phase rails, on the other hand, rely on a three-phase power supply, offering greater power capacity and flexibility, which is well suited to larger commercial, retail and industrial applications. Understanding these power differences is essential to selecting the right track lighting system to meet the specific lighting needs of your space.
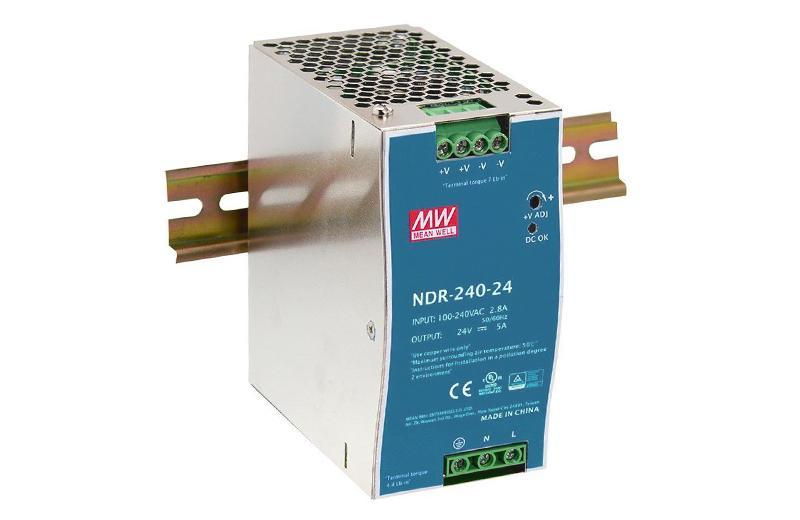

>24 VDC LED POWER SUPPLY, 240VA
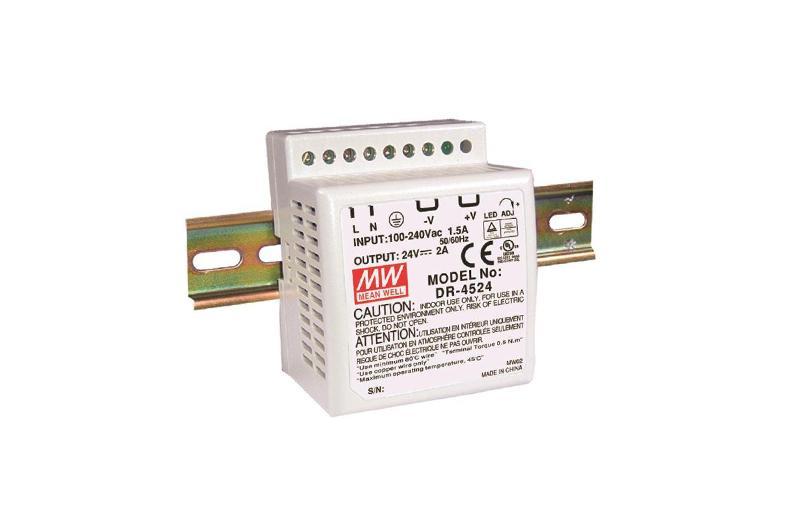

> 24 VDC, POWER SUPPLY, 45VA
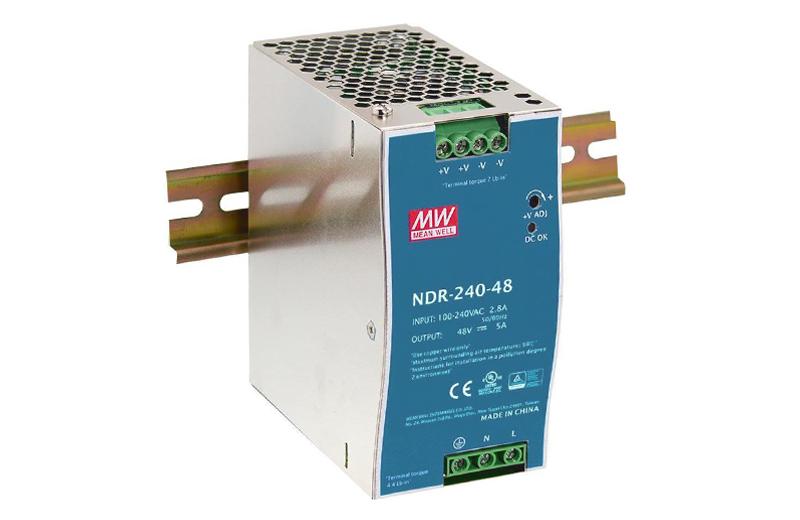

> 48 VDC POWER SUPPLY, 240VA
> 5. ADAPTERS AND RAIL LIGHTING
Track lighting has revolutionized the way we illuminate spaces, offering both functionality and aesthetics. Two essential components that significantly enhance the versatility of track lighting are track fixtures with in-track adapters and those with on-track adapters. These fixtures, equipped with the right adapters, provide creative solutions for tailored lighting designs, making it easier to achieve your desired ambiance and functionality. Let’s delve into the features and benefits of them:
Seamless Continuity: These fixtures are specifically designed to integrate smoothly with the track layout. The in-track adapters ensure a seamless transition between the fixture and the track, both electrically and aesthetically. This means there are no unsightly gaps or visible connectors, maintaining the clean and minimalist appearance of your lighting design.
Flexible Placement: Fixtures with both adapters are highly flexible when it comes to placement. You can click them in the track at any desired position, allowing for easy adjustments and customization of your lighting layout. This adaptability is ideal for spaces where the lighting requirements may change frequently.
Streamlined Appearance: In-track fixtures offer a sleek and unobtrusive look. They blend seamlessly with the track, which is particularly appealing in modern and minimalist interior designs. The focus remains on the illumination rather than the fixtures themselves.
Electrical Continuity: both adapters not only ensure visual continuity but also maintain electrical connectivity. This ensures that the fixture receives power consistently, providing stable and reliable lighting throughout the track.
Built-in drivers: many of the larger fixtures have an internal driver which, among other things, rectifies a higher voltage, which alternate the current to low-voltage, on which the fixture operates. This doesn’t fit in the smaller fixtures, then its placed in an on-track adapter, or it is connected to the track.
In summary, track fixtures with in-track and on-track adapters offer versatile solutions for customized lighting designs. In-track adapters ensure a seamless and integrated look with consistent electrical connectivity, making them ideal for maintaining a clean and modern aesthetic. On the other hand, fixtures with on-track adapters provide flexibility and a wide range of fixture options, allowing for easy adjustments and customization to meet various lighting needs and design preferences. Whether you prioritize a streamlined appearance or the ability to change and adapt your lighting layout with ease, both options offer valuable tools to achieve your lighting vision.
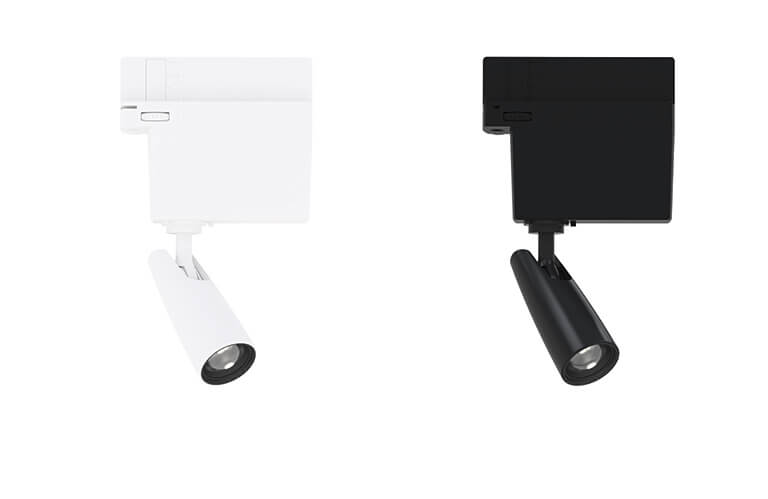

> On-track adapter
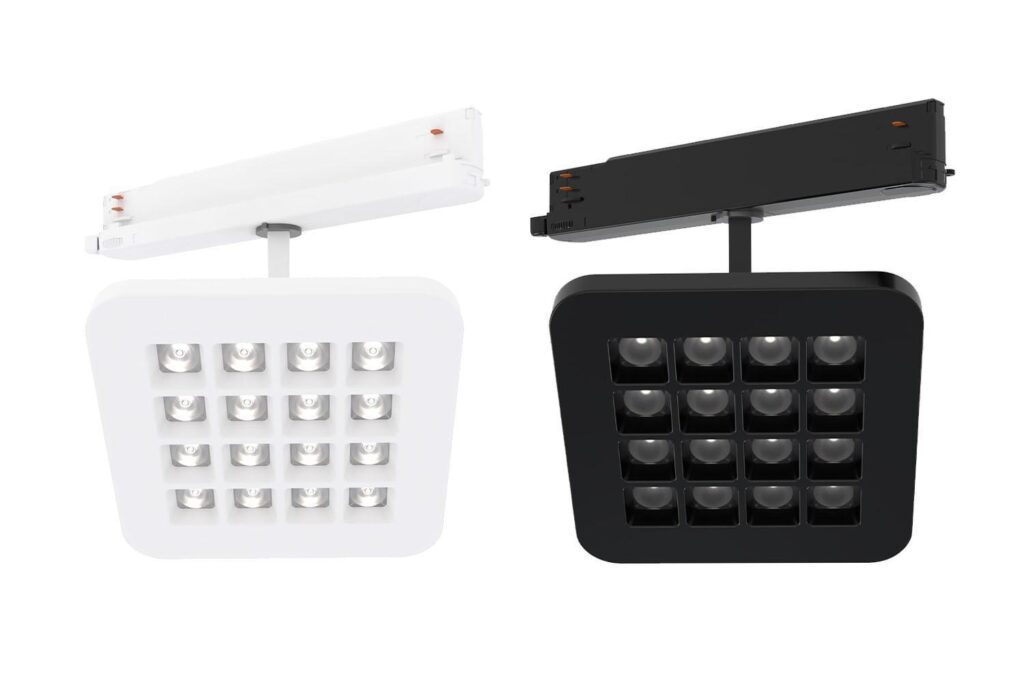

> in-track adapter
> 6. DMX AND RAIL LIGHTING
There are a few things to keep in mind when you are going to install DMX controlled track fixtures. These are a few of them:
- Do not create a ‘ground wire loop’
- Don’t add too many fixtures on a rail to ensure optimal performance
- Use a current limiter to prevent blowing fuses
- Prevent disturbances by using a max. consecutive track length of 20m
To know all about DMX and track lighting, read our page ‘How to set up DMX controlled CLS fixtures‘.

stay up to date with our newsletter
> WANT TO KNOW MORE ABOUT TRACK LIGHTING?
Want to know more about track and compatible fixtures? Look at our product pages to see which products are compatible with track, or contact us. We are happy to help.
